I was using ChatGPT for some of my causal queries. I realized that it is a trained model, it is trained on the huge collection of internet data using supercomputers.
What happens if we ask a question to this language model on data or information that it has not been specifically trained on?
I asked ChatGPT about Chroma DB, and here's what it said! 😅.

ChatGPT is a trained model with vast amounts of internet data and is highly proficient in contextual understanding. So it can be used for various applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, customer support systems, and more.
Even we can use this model on our own custom dataset for our own use cases.
Companies can utilize this model to train it on their own data and employ it as a chatbot, enabling responses generated from the trained dataset.
Let's try to build a doc-chat(chat with your document) app ⚒️.
Let's utilize a PDF file to train the GPT model and enable it to engage in chat conversations.
I have created a flow diagram to offer a clearer understanding of the application we are going to build now.
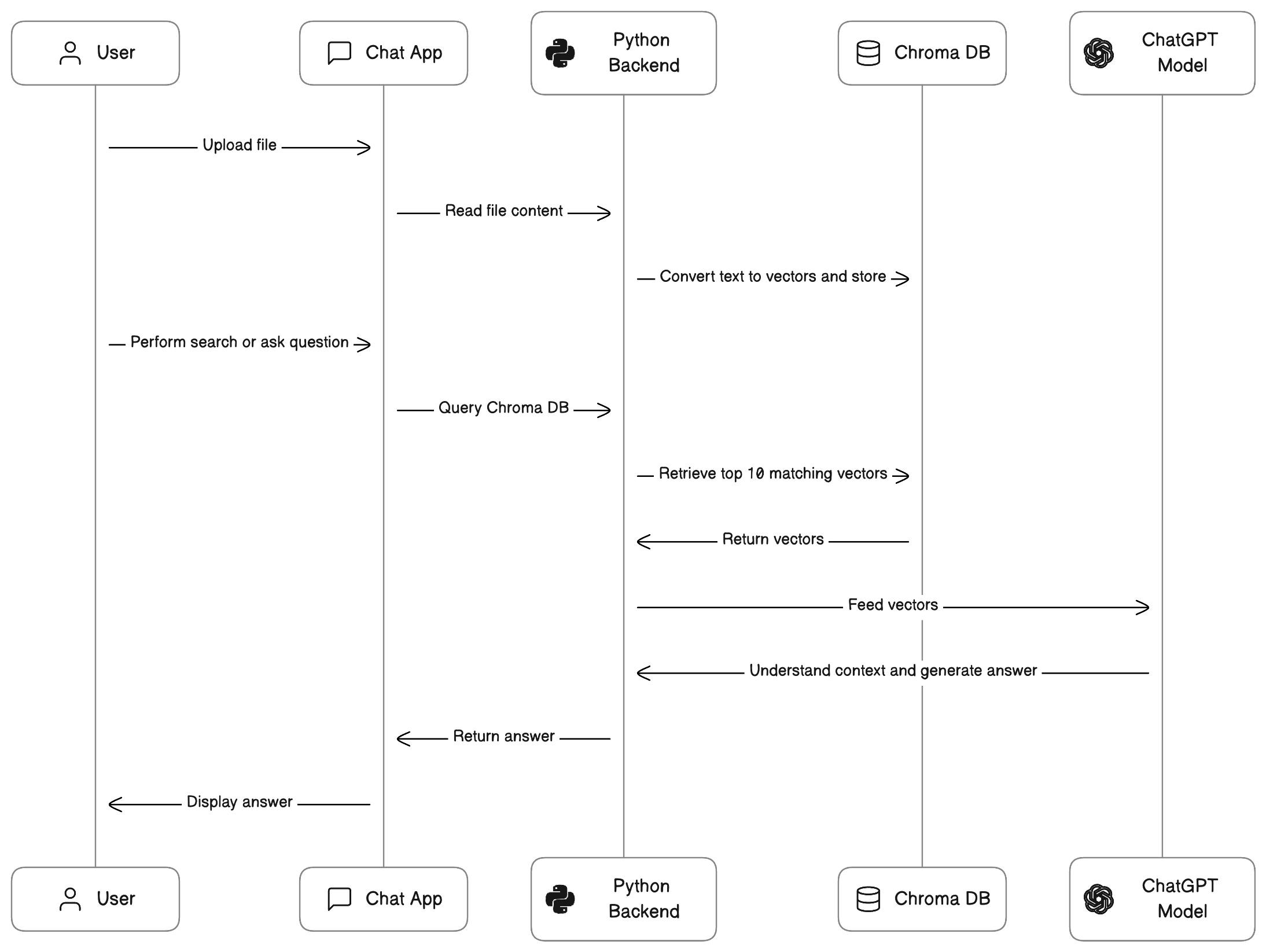
Let's break down the above flow diagram into words:
We use Python to read PDF files and store them in a 'vector database' called Chroma DB.
Vector search databases are useful for applications that require search suggestions and recommendations.
In our case, we read PDF documents, convert them to vectors, and save these vectors in the database. Using these vectors, we can perform search operations on related data.
When a user asks a question, we query the vector database to retrieve the most relevant fields from the documents.
After obtaining highly related information based on the searched key, we can use the ChatGPT model to better understand the context of the data.
By providing the model with this retrieved search information, it gains an understanding of the data's context.
Once the model understands the context, we can ask any question related to the retrieved information.
Let's do some coding 👨💻.
We gonna use the following stack for our project:
Python.
Chroma DB (vector search database).
OpenAI
embedding modelAPI to convert text to vectors.OpenAI
gpt-3.5-turboAPI to generate the relevant response/chats.
Let's import some modules.
import os
from pypdf import PdfReader
import openai
import chromadb
from chromadb.utils import embedding_functions
import random
Process the PDF content to vectors and store it in DB.
client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path=chromadb_path)
openai_ef = embedding_functions.OpenAIEmbeddingFunction(api_key=openai_api_key, model_name=openai_model_name)
collection = client.get_or_create_collection("my_searchable_collection", embedding_function=self.openai_ef)
def save_data_to_chrom_db(text_chunks):
try:
for text in text_chunks:
collection.add(documents=text.strip(), ids=[str(random.randint(1, 1000000))])
except Exception as e:
print('error:======', e)
def pdf_handler(file_path):
reader = PdfReader(file_path)
page = reader.pages[0]
text_line_by_line = []
for i in range(len(reader.pages)):
page = reader.pages[i]
# extract the text line by line and save it in the array lines
lines = page.extract_text().splitlines()
filtered_lines = [item for item in lines if item.strip()]
text_line_by_line.extend(filtered_lines)
save_data_to_chrom_db(text_line_by_line)
First, we create the DB client connection.
This client accepts two parameters: the name of the
collectionto store the data and anembedding_functionthat converts the text to vectors before saving the data.If we don't pass the
embedding_functionexplicitly Chroma DB uses the Sentence Transformersall-MiniLM-L6-v2model to create embeddings.In our case, we are utilizing OpenAI's embedding model API to perform vector embedding. We achieve this by instructing the
chromadb.utilshelper function by providing theopenai_efhelper function, which is connected to OpenAI's embedding model API using the appropriate API key.In the next step, the
pdf_handlerfunction reads the file data line by line and creates small chunks of text. These chunks are then passed to thesave_data_to_chrom_dbfunction, where they are converted into vectors and stored in the database.
We create a search function that reads the data from the database and passes it to the GPT model. By doing so, we aim to retrieve more relevant and meaningful information based on the user's queries or questions.
def search_data_from_chrom_db(text):
try:
search_result = collection.query(query_texts=[text], n_results=10)
return search_result.get("documents")[0]
except Exception as e:
print('error:======', e)
def handleSearch(search_text):
search_result = search_data_from_chrom_db(search_text)
prompt = f"consider these statements this are search results from the db {search_result}. \
\n Please give me the related information that the search results have about {search_text} in a short and descriptive way as an answer to user and avoid additional sentences in the responce."
openai.api_key = openai_key # pass your generated openai key
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
search_data_from_chrom_db(text): This function searches the database (Chroma DB) for documents related to the giventext. It queries the database and returns the most relevant document based on the search text.handleSearch(search_text): This function handles the search process. It callssearch_data_from_chrom_dbto get the relevant data from the database based on thesearch_text. It then forms a prompt using this data and sends it along withsearch_textto GPT-3.5 Turbo model.prompt: The prompt is the instruction given to the GPT model. It asks the question provided by the user, and it includes the context obtained from the search results retrieved from Chroma DB. By combining the user's question and the context of the data, the prompt guides the GPT model to generate a relevant and concise answer from the document that we used.
Conclusion:
We can use the ChatGPT model on our own custom data by combining it with your database and user inputs. Here's a brief overview of the steps:
Set up a database to store custom data. In this case, we used Chroma DB to store PDF vector data.
Create functions to handle data processing. In our case, we have a function (
pdf_handler) to read PDF files and convert them into vectors, which are then stored in the database.Implement a search function (
search_data_from_chrom_db) to query the database and retrieve relevant data based on user input.Construct a prompt that includes the user's question and the context from the retrieved data. This prompt is used to instruct the ChatGPT model and generate a response relevant to the user's query.
By passing the prompt to the model, we can obtain a response that combines the user's query and the context provided by the database.
You can find this entire code in my repo : github.com/Basavarajrp/Doc-GPT-App
Feel free to connect and share your valuable inputs in the comment section. See you all in the next blog! 👋.
Tq, Happy Coding 👨💻.
